2Department of Biophysics, Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam University Faculty of Medicine, Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye
3Department of Biochemistry, Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam University Faculty of Medicine, Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye
4Department of Pathology, Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam University Faculty of Medicine, Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye
5Department of Cardiology, Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam University Faculty of Medicine, Kahramanmaraş, Türkiye
Abstract
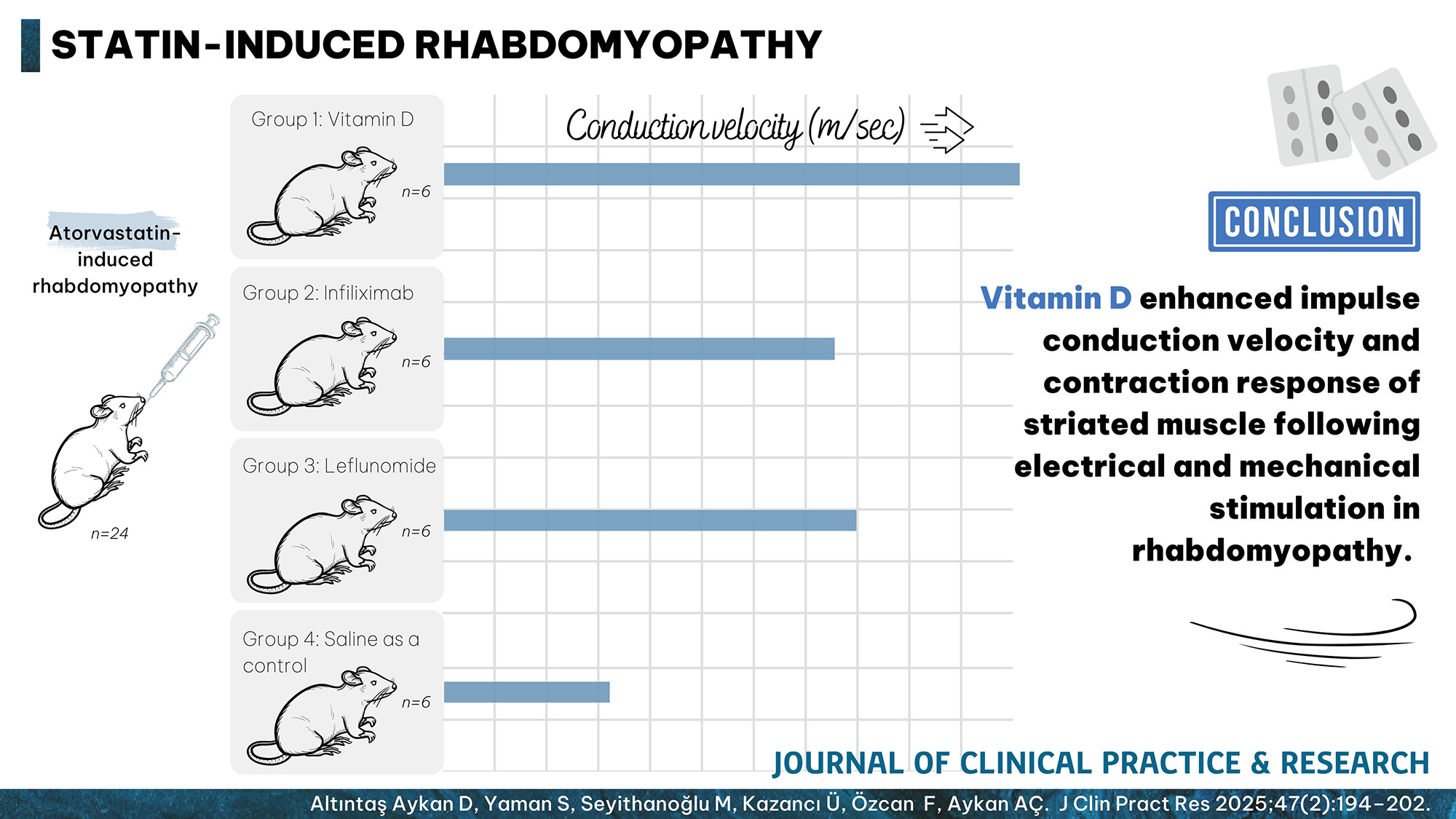
Objective: The most common adverse effects of statins are muscle disorders. This study investigated the effects of vitamin D, infliximab, and leflunomide on statin-induced rhabdomyopathy by evaluating myofibrillar contractions under electrical and mechanical stimulation.
Materials and Methods: Twenty-four rats were induced rhabdomyopathy using atorvastatin (100 mg/kg/day for three weeks). The rats were then divided into four groups: Group 1 (n=6) received vitamin D (0.2 µg/kg), Group 2 (n=6) received infliximab (7 mg/kg), Group 3 (n=6) received leflunomide (10 mg/kg), and Group 4 (n=6) received saline as a control. In vitro organ bath experiments were performed using electrical and mechanical stimulations on the isolated extensor digitorum longus muscle to assess contraction responses. Blood and tissue samples were analyzed for creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and malondialdehyde (MDA).
Results: Group 1 demonstrated significant improvements in contractile responses (Twitch: Group 1 vs. Group 2, p=0.004; Group 1 vs. Group 3, p=0.025; Group 1 vs. Group 4, p<0.001. At 20 Hz: Group 1 vs. Group 2, p=0.018; Group 1 vs. Group 4, p=0.001; Group 3 vs. Group 4, p=0.015. At 80 Hz: Group 1 vs. Group 2, p=0.008; Group 1 vs. Group 3, p=0.0016; Group 1 vs. Group 4, p<0.001. At 100 Hz: Group 1 vs. Group 2, p=0.006; Group 1 vs. Group 3, p=0.015; Group 1 vs. Group 4, p<0.001). At 40–60 Hz and 120–140 Hz, Groups 1, 2, and 3 showed higher responses than Group 4 (p<0.05). Impulse conduction velocity in Group 1 was higher than in Group 4 (p=0.019). Group 1 exhibited significant differences in renal GPx (Group 1 vs. Group 3, p=0.023) and MDA (Group 1 vs. Group 2, p=0.001; Group 1 vs. Group 3, p=0.003). Additionally, Group 1 showed significant improvements in histopathologic evaluation compared to the control group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Vitamin D enhanced impulse conduction velocity and contraction response of striated muscle following electrical and mechanical stimulation in rhabdomyopathy. Monitoring vitamin D levels in dyslipidemic patients may serve as a predictive marker for adverse effects of statins. Providing these patients with vitamin D supplementation may improve statin intolerance.
Graphical Abstract